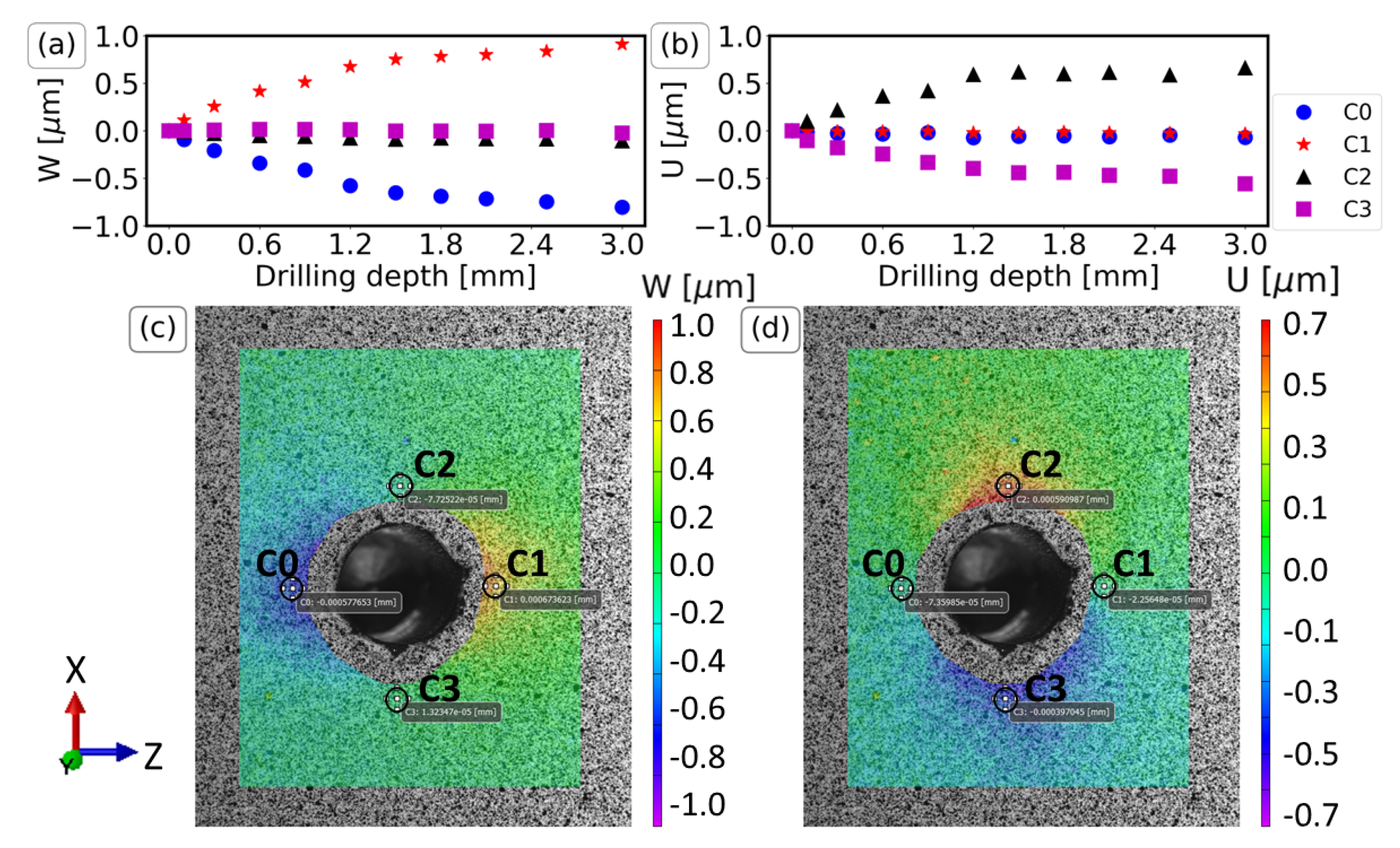
FOV Ranges for Stereo-DIC
The standard FOV ranges from 40 to 400 mm, 4, 8 and 16 m can be extended to very large FOVs not only using multiple stereo systems in combination but also by a single stereo system. Therefore, VIC offers special calibration methods for large and very large FOV measurements that exceed the size of the hand-held calibration panels (> 1 m). We offer the suitable lenses and the required hardware such a battery driven systems or water protection even for under water applications.
Wind Turbine Blade (FOV > 100 m)
Special systems for outdoor applications, such as for measuring bridges or (rotating) wind turbines blades with Ø > 100 m are available with camera distances of 200 m, controlled from a Laptop operating on battery power. Measurements by Jan Windstroth, Hannover University, Institute for Turbomaschinery and Fluid Dynamics, Germany.
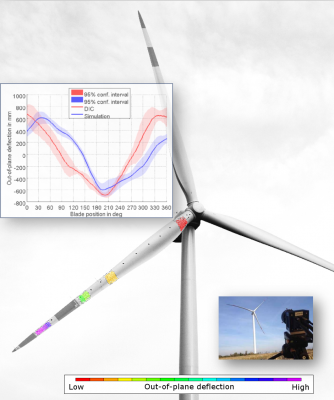
Below: Feasibility of the measurement in a model study back in 2013. Measurements by Jan Windstroth, Hannover University, Institute for Turbomaschinery and Fluid Dynamics, Germany.
Outdoor Wave Measurement ( FOV 75 m x 30 m)
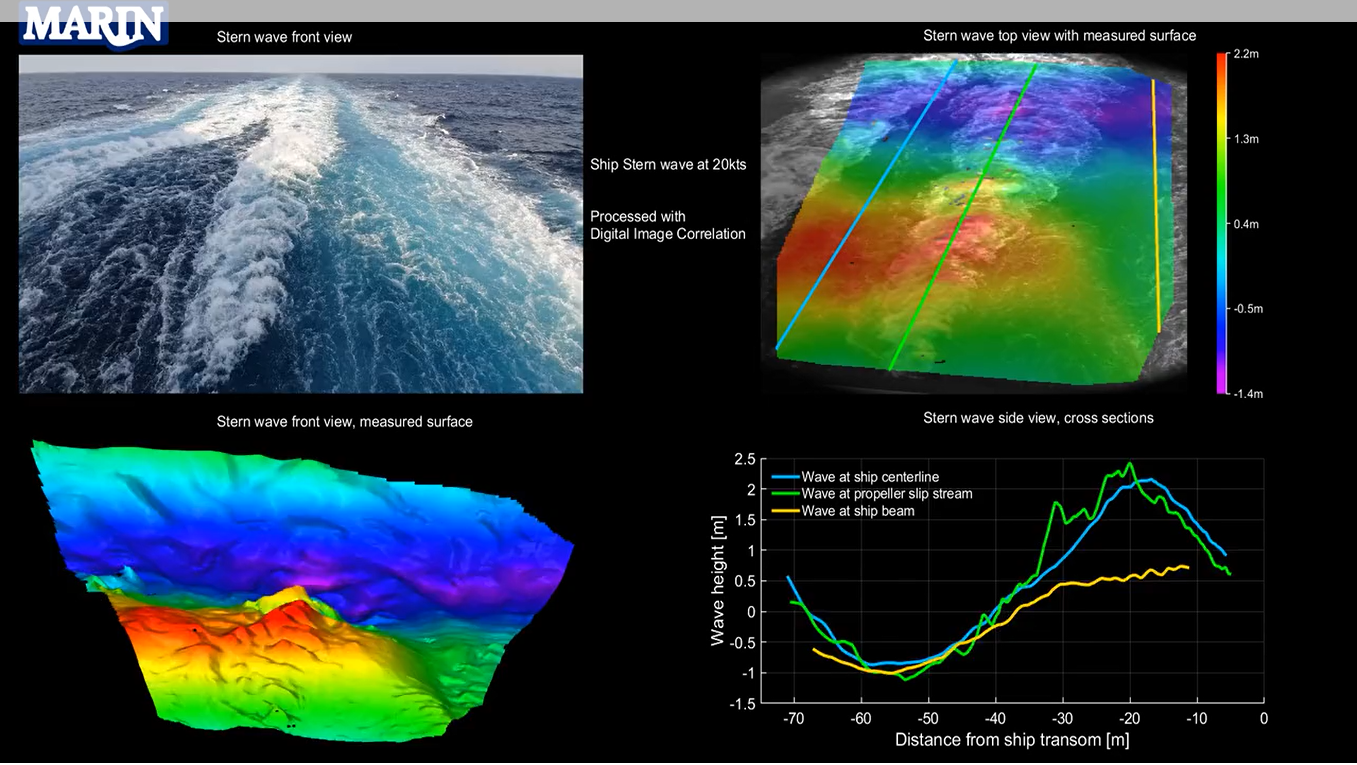
Full Scale CFD Validation using Ship Performance and Wave Pattern Measurements of a Mega Cruise Ship
Another application, in collaboration with the Maritime Research Institute of Netherlands, involved recording the wave formation behind a 330 m long cruise ship sailing at 20 knots. Start the video of the stern wave measurement (Video generated within VIC iris workspace by Marin.NL).
Sources:
(1)https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/OMAE/proceedings-abstract/OMAE2022/85925/V007T08A041/1147961
(2)https://www.marin.nl/en/news/full-scale-cfd-validation-using-ship-performance-and-wave-pattern-measurements-of-a-mega-cruise-ship
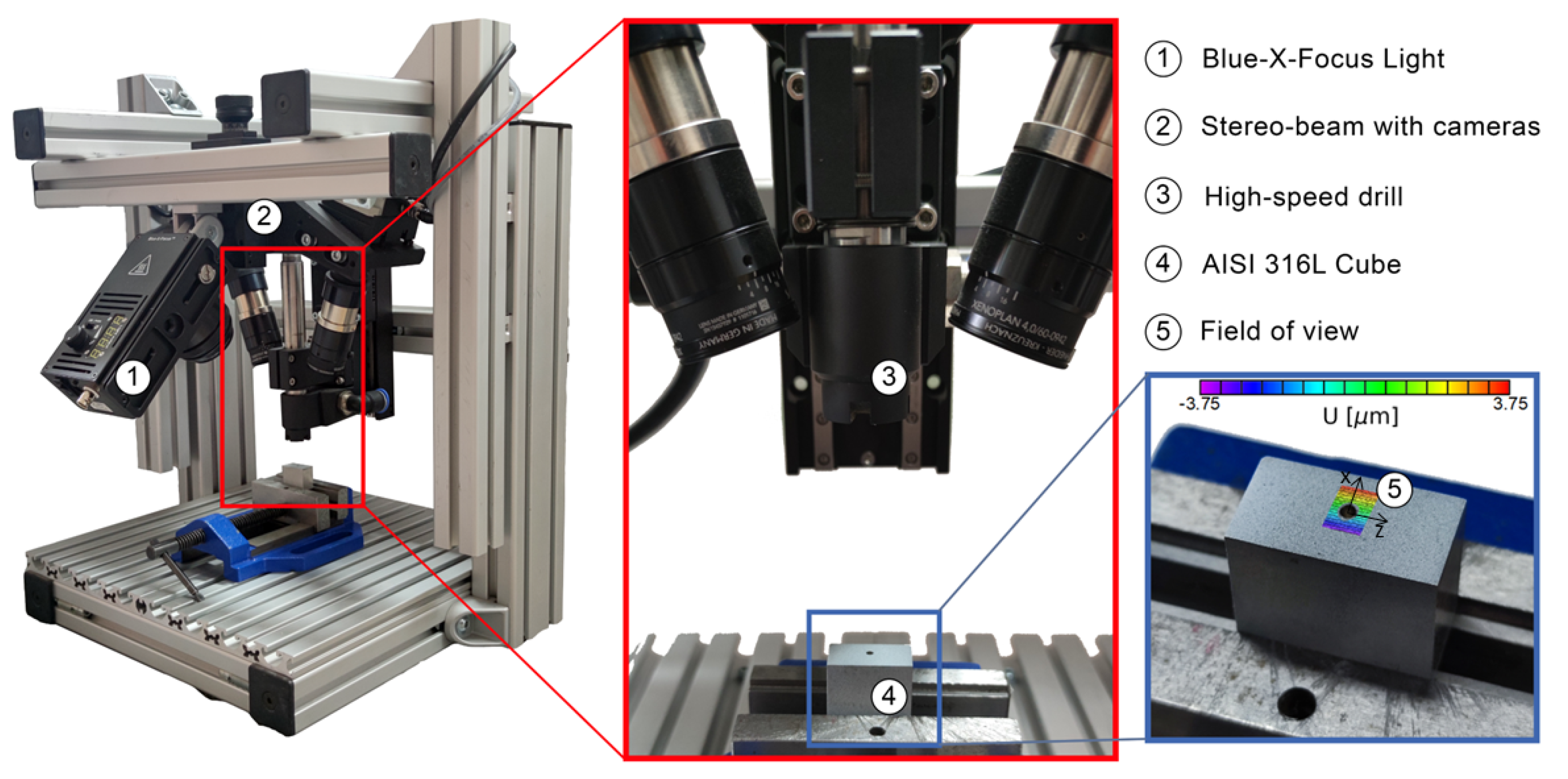
Long Distance Small FOV (Stereo-DIC)
Outdoor measurement on small field of view (FOV) at long working distance with high sensitivity and/or accuracy require not only special calibration methods for 2D and 3D applications but also special recording and evaluation methods, as these application underlaying high noise influences such as thermal air waves resulting into optical Schlieren.